EarthCARE goals
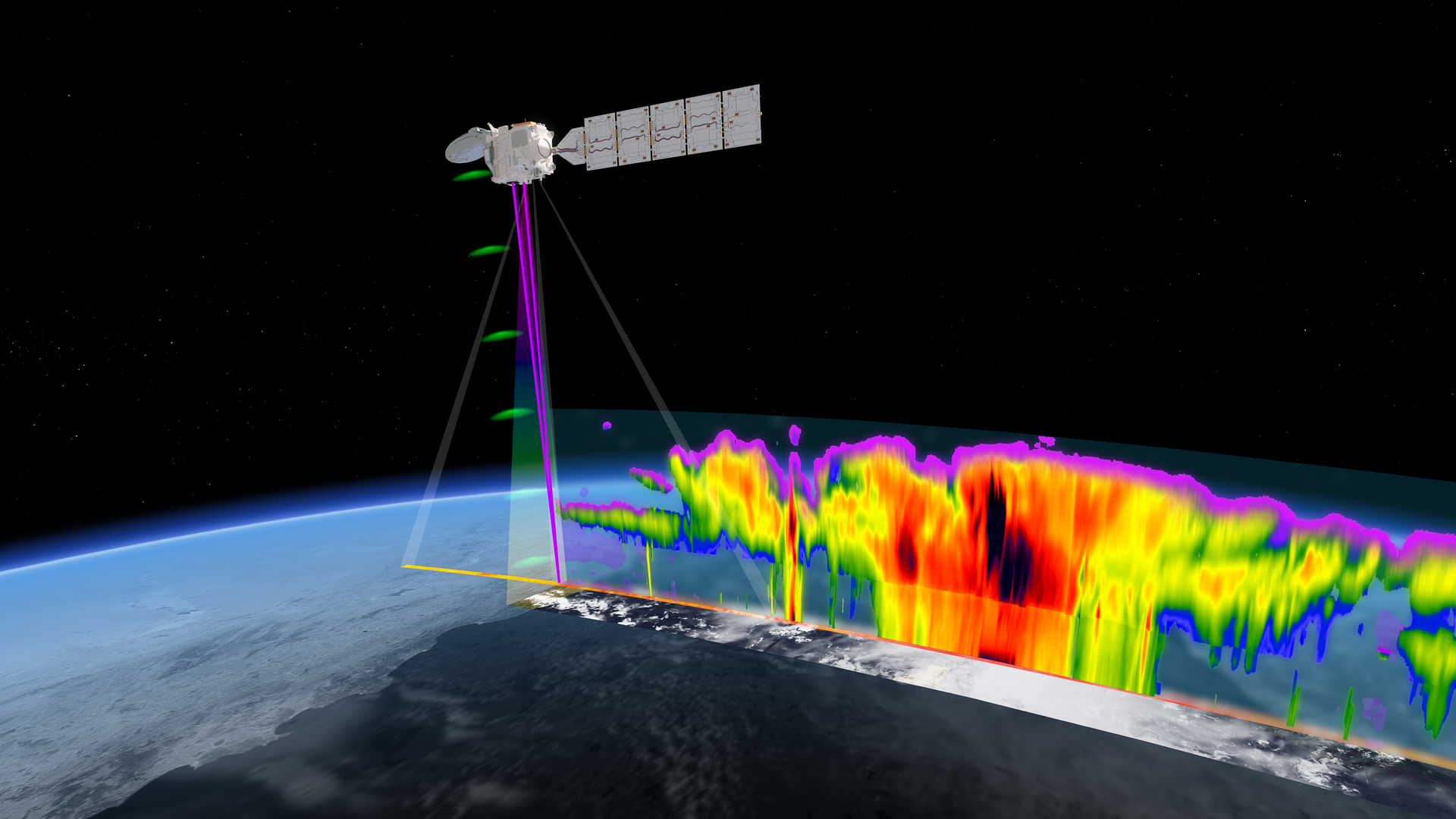
EarthCARE has been designed to measure the 3D structure of cloud and aerosols, together with collocated observations of solar (shortwave) and terrestrial (thermal) radiation to shed new light on the role that clouds and aerosols play in regulating Earth’s temperature.
Specifically, the goal of EarthCARE is to quantify cloud–aerosol –radiation interactions so they can be included in climate and numerical weather forecasting models.
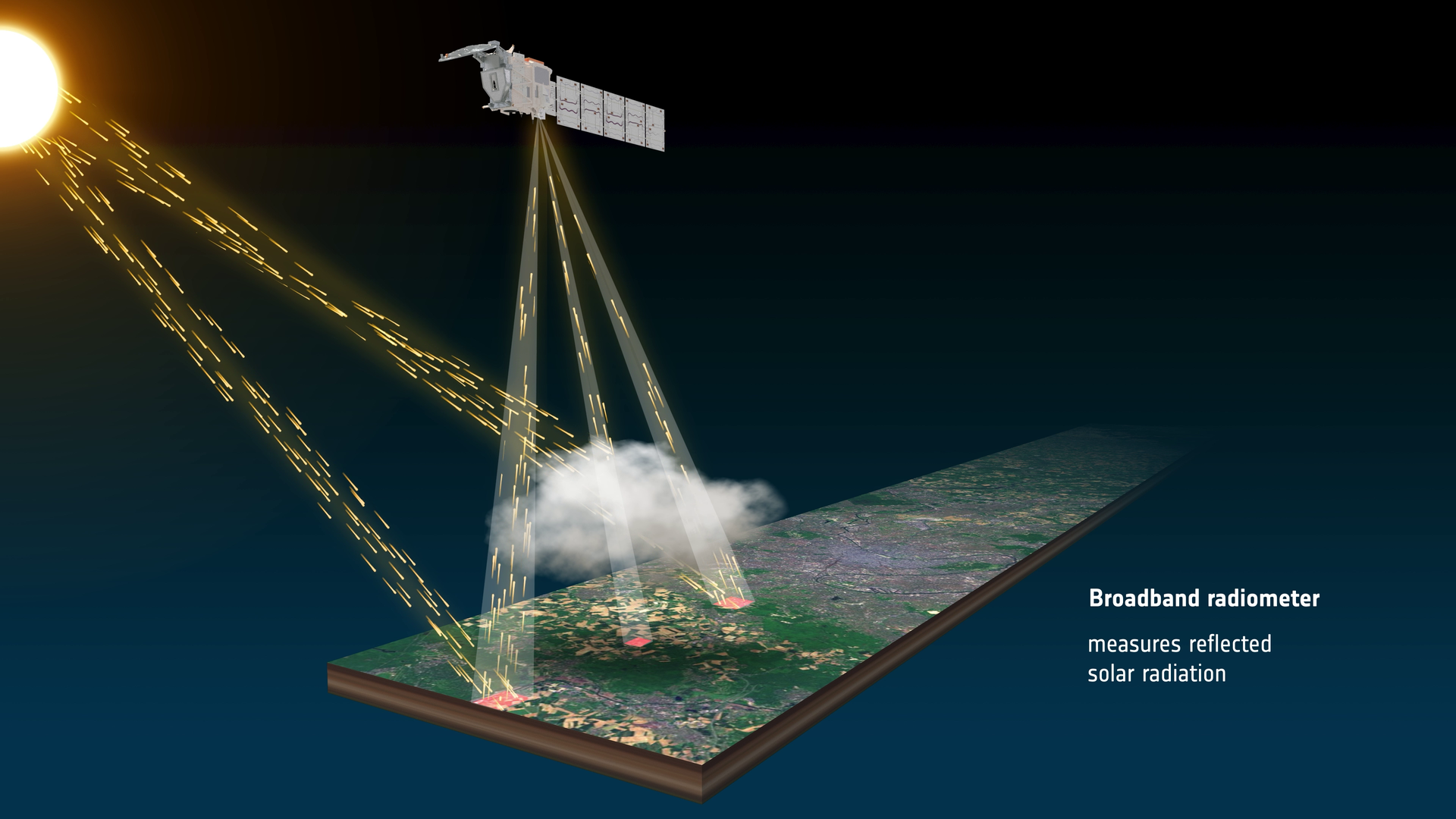
To achieve this, the satellite carries four scientific instruments, two active instruments: a lidar and a radar to measure the vertical distribution of clouds and aerosols, and two passive instruments: an imager to collect cloud and aerosol information across the satellite ground track and a broadband radiometer to measure outgoing reflected solar and emitted thermal radiation at the top of the atmosphere.
The scientific objectives of the mission are:
- To observe vertical profiles of natural and anthropogenic aerosols on a global scale, their radiative properties and interaction with clouds
- To observe vertical distributions of atmospheric liquid water and ice on a global scale, their transport by clouds and their radiative impact
- To observe cloud distribution, cloud-precipitation interactions and the characteristics of vertical motions within clouds
- To retrieve profiles of atmospheric radiative heating and cooling through the combination of the retrieved aerosol and cloud properties.
EarthCARE measurements will link cloud, aerosols and radiation at a target accuracy of 10Wm-2. The mission will achieve these objectives by measuring globally the vertical structure and horizontal distribution of cloud and aerosol fields together with outgoing radiation. Specifically, EarthCARE will measure:
- Properties of aerosol layers: occurrence, extinction profiles, boundary layer height, distinction of aerosol types
- Properties of cloud fields: cloud boundaries and multilayer clouds, height-resolved fractional cloud cover and overlap, occurrence of liquid/ice/super-cooled layers, vertical profiles of ice water content and effective particle size, vertical profiles of liquid water and effective droplet size, and small-scale (<1km) fluctuations of these properties
- Vertical velocities to characterise cloud convective motion and ice sedimentation
- Drizzle rain rates and estimates of heavier rainfall rates
- Reflected solar and emitted thermal radiances at the top of the atmosphere.