In-Orbit Manufacturing of Very Long Booms
| Programme: | GSTP | Achieved TRL: | 3 |
| Reference: | G617-083MS | Closure: | 2015 |
| Contractor: | Magna Parva (UK) | ||
Many space applications require large structures in space - typical examples include satellites for telecommunication or earth observation. As the requirements for larger arrays and booms increases, the mass of the structure goes up and the complexity of the deployment mechanism increases. One solution is to manufacture structures in space using a simple technology that can produce high quality, large structures in an autonomous fashion.
Objectives
The main objective of the activity was to develop a technology allowing in-orbit manufacturing of very long, slender composite booms for large aperture applications. The activity included the realization of a prototype BB pultrusion machine to be operated in vacuum in order to demonstrate the feasibility of the in-orbit boom production. Short length booms (length to be determined by test facility) have been produced and mechanically tested.
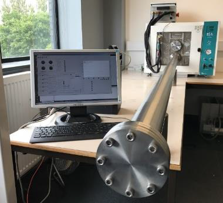
Achievements and status
The activity included the realization of a prototype BB Pultrusion Machine operated in vacuum, demonstrating the feasibility of the technology. Booms were produced and mechanically tested (tensile, flexural, compressive, porosity, thermal, quality of cure). In most cases, the Coefficient of Variation of data obtained approaches seen in the commercial aerospace environment.
The activity included the realization of a prototype BB Pultrusion Machine operated in vacuum, demonstrating the feasibility of the technology. Booms were produced and mechanically tested (tensile, flexural, compressive, porosity, thermal, quality of cure). In most cases, the Coefficient of Variation of data obtained approaches seen in the commercial aerospace environment.
Benefits
The pultrusion process utilises a supply of fibre reinforcement tows and resin matrix system to manufacture (‘pultrude’) constant cross-section composite structures of nearly-indefinite length. The technology is most effectively employed in space system applications of around 40 m in size, at which point conventional deployer technology is outperformed due to launch, test and operation constraints.
Next steps
A Luxemburg national activity (LuxImpulse) will continue to extend the TRL to TRL 6 by Q4 2018. This includes the development of the first application. Flight qualification for the technology is currently planned to be achieved through deployment on the first satellite of the radio transmission interferometry/geolocation mission for approximately Q4 2019.





